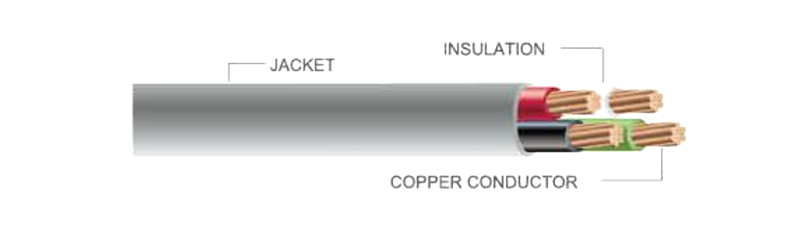
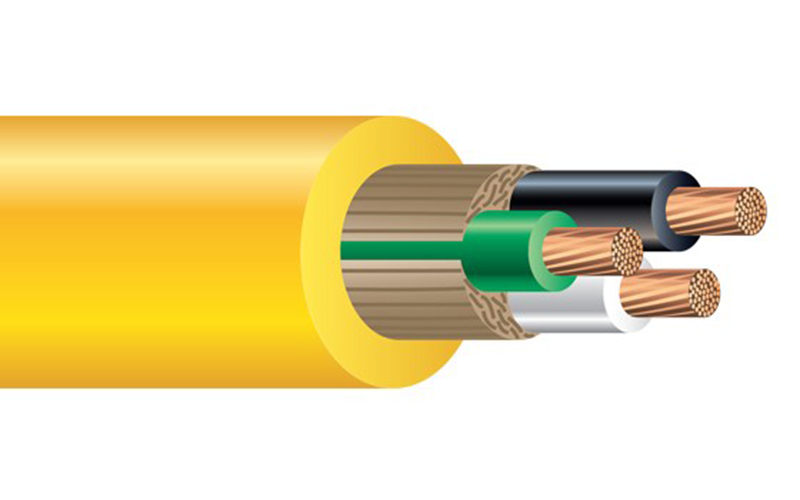
Selecting the right flexible cable can be challenging, as different cable types are designed for very different applications. Flexible cables range from extension cords, which lengthen a power connection when an outlet is out of reach, to computer power cords that link a power supply unit to internal components. In large-scale projects such as construction or industrial installations, bulk flexible cable is commonly used, allowing installers to cut custom lengths for specific needs. Flexible cords may also serve as appliance cables or data and power transmission lines, making proper selection essential for safety and performance.
To choose the suitable flexible cable, several key factors should be considered:
Insulation Type
Cable insulation determines resistance to moisture, chemicals, abrasion, and heat. PVC insulation is widely used for general purposes due to its affordability and durability, but it may not perform well in high-temperature or oil-exposed environments. Selecting insulation that matches the operating conditions helps extend cable life.
Wire Size (Gauge)
Wire gauge directly affects how much current a cable can safely carry. Thicker conductors (lower gauge numbers) handle higher loads with less heat buildup, while thinner wires are more prone to overheating. Matching wire size to the circuit’s current and voltage requirements is critical to preventing electrical hazards.
Temperature Rating
Each flexible cable is rated for a specific temperature range. Using a cable outside its rated limits can cause insulation breakdown, reduced performance, or failure. Always choose a cable designed to tolerate the environmental temperatures where it will be installed.
Voltage Rating
Voltage ratings indicate the voltage a cable can safely handle. A cable rated too low risks insulation damage and failure, while excessively high ratings may add unnecessary cost. The goal is to match the cable’s voltage rating to the application.
Durability
Flexible cables often experience frequent bending, movement, and mechanical stress. Heavy-duty designs are built to withstand repeated use without cracking or conductor fatigue. Choosing a durable cable reduces maintenance, improves safety, and lowers long-term replacement costs.
By evaluating these factors together, you can select a flexible cable that delivers reliable performance, long service life, and safe operation for your specific application.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体













 NO.565,South of Xihuan Rd,Yuyao City Zhejiang China.
NO.565,South of Xihuan Rd,Yuyao City Zhejiang China. 0086-574-62599999/62593088
0086-574-62599999/62593088 0086-574-62598888
0086-574-62598888 ryan.yu@nbwell.com
ryan.yu@nbwell.com